

植物学报 ›› 2016, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 107-119.DOI: 10.11983/CBB15059
收稿日期:2015-03-26
接受日期:2015-07-17
出版日期:2016-01-01
发布日期:2016-02-01
通讯作者:
鲁迎青
作者简介:? 共同第一作者
基金资助:Zhixin Zhu1,2, Yingqing Lu1*
Received:2015-03-26
Accepted:2015-07-17
Online:2016-01-01
Published:2016-02-01
Contact:
Lu Yingqing
About author:? These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要: 花青素是种子植物呈色的重要色素, 由一系列结构基因编码的酶(CHS、CHI、F3H、F3'H、F3'5'H、DFR、ANS和3GT)催化而成, 随后经过各种修饰被转运至液泡等部位储存。各类器官中差异表达的MYB、bHLH和WDR三种调控因子通过形成MBW复合体直接正调控以上结构基因的表达。这个过程涉及的基因变异常会导致植物的各种颜色变异。在生活中人们广泛利用这些变异品种, 取其丰富色味。造成颜色变异的具体分子机制在很多情况下还不清楚, 但日益积累的个例研究为其中的规律性提供了基础数据。该文概述了花青素的合成、转运过程及其转录调控机制, 探讨了研究颜色变异品种的常用思路及方法。在总结近年工作的基础上, 对生活中常见蔬菜、水果和花卉的颜色变异品种的分子机制进行了综述。
祝志欣, 鲁迎青. 花青素代谢途径与植物颜色变异. 植物学报, 2016, 51(1): 107-119.
Zhixin Zhu, Yingqing Lu. Plant Color Mutants and the Anthocyanin Pathway. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(1): 107-119.
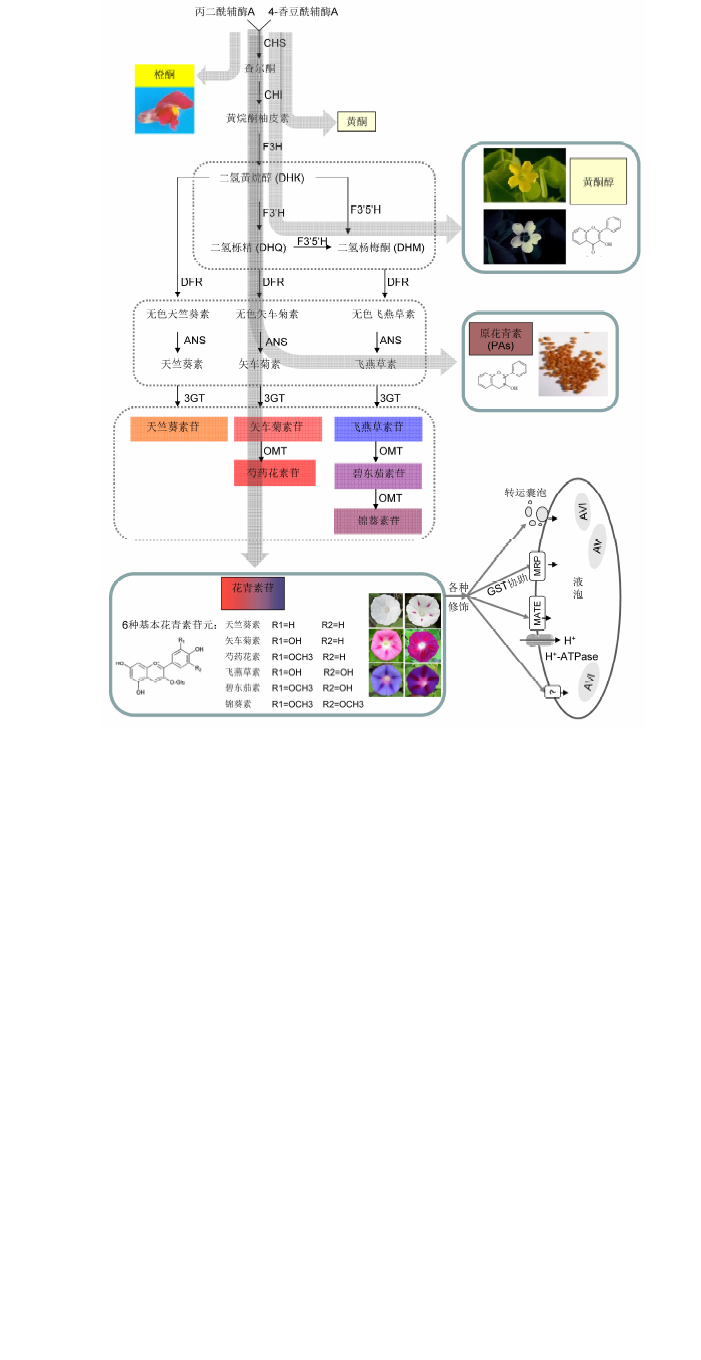
图1 类黄酮代谢途径中花青素的合成示意图 花青素合成途径的中间底物也可被导向类黄酮途径的其它分支(灰色箭头所示)。
Figure 1 The flavonoid biosynthetic pathway leading to the production of anthocyaninThe intermediate substrates can be canalized to other branches of the flavonoid pathway, which were indicated with grey arrows.
| 物种 | 花青素相关MBW复合物的成员 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MYB | bHLH | WDR | |
| 玉米(Zea mays) | ZmC1, ZmPl | ZmR, ZmB | ZmPAC1 |
| 拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana) | AtPAP1, AtPAP2 | AtGL3, AtEGL3 | AtTTG1 |
| 矮牵牛(Petunia hybrida ) | PhAN2, PhAN4 | PhAN1 | PhAN11 |
| 圆叶牵牛(Ipomoea purpurea) | IpMYB1 | IpbHLH2 | IpWDR1 |
表1 常见模式研究物种中花青素相关MBW复合物的成员
Table 1 Members of the MBW complex in anthocyanin model species
| 物种 | 花青素相关MBW复合物的成员 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MYB | bHLH | WDR | |
| 玉米(Zea mays) | ZmC1, ZmPl | ZmR, ZmB | ZmPAC1 |
| 拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana) | AtPAP1, AtPAP2 | AtGL3, AtEGL3 | AtTTG1 |
| 矮牵牛(Petunia hybrida ) | PhAN2, PhAN4 | PhAN1 | PhAN11 |
| 圆叶牵牛(Ipomoea purpurea) | IpMYB1 | IpbHLH2 | IpWDR1 |
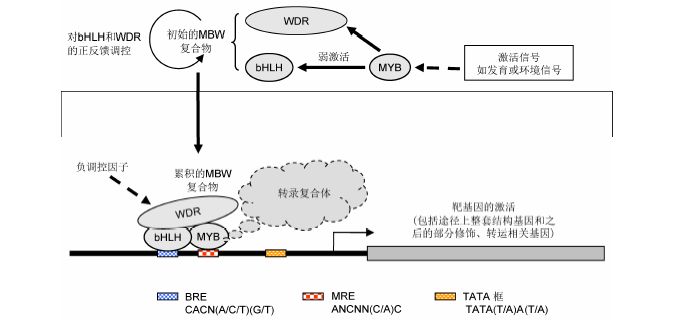
图2 花青素代谢途径转录激活假说示意图 花青素相关MYB被诱导表达后, 可反馈性激活bHLH和WDR的表达, 并组成MBW复合物。MBW复合物的激活能力显著高于MYB本身, 其靶基因包括花青素合成途径的整套基因和之后的部分修饰与转运相关基因。MBW复合物对应2个识别序列, 分别为MRE (MYB识别序列)和BRE (bHLH识别序列), 它们分别遵循ANCNN(C/A)C和CACN(A/C/T)(G/T)序列模式(Zhu et al., 2015)。不论是MBW复合物功能异常, 还是靶基因启动子上MRE和BRE序列突变, 都可能导致花青素的合成异常。
Figure 2 The hypothesized regulatory mechanism for the activation of the anthocyanin pathwayOnce the anthocyanin MYB was induced by signals, it may activate the expression of bHLH and WDR, forming the MBW complex all together. The MBW complex has much higher activation ability than MYB alone. The targets of the MBW complex include the whole set of the core structural genes of the anthocyanin pathway, and likely also comprising genes encoding relevant modification and transportation enzymes. There were two classes of cis elements for the MBW complex, the MRE (MYB-recognizing elements) and BRE (bHLH-recognizing elements), which were in the form of ANCNN(C/A)C and CACN(A/C/T)(G/T) respectively (Zhu et al., 2015). Either the functional disorder of the MBW complex or the mutations at MRE or/and BRE of the target promoters may cause abnormal anthocyanin biosynthesis.
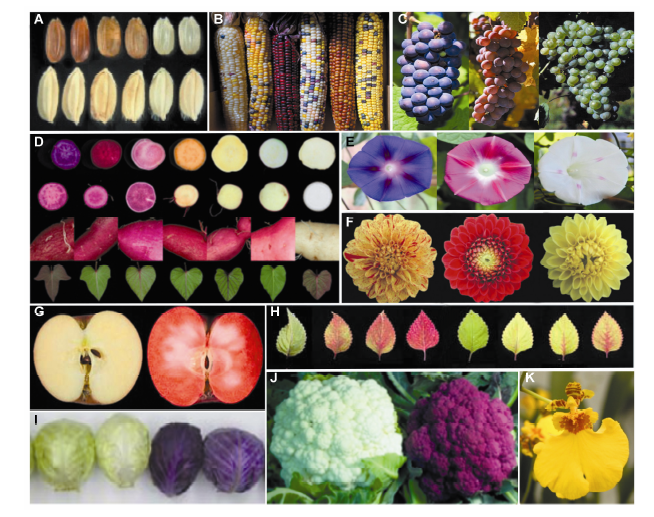

图4 生活中与花青素代谢途径相关的常见颜色变异品种(部分图改自相应参考文献) (A) 水稻红米(Furukawa et al., 2007); (B) 杂色玉米(Lazarow et al., 2013); (C) 紫皮、绿皮葡萄; (D) 紫薯(Mano et al., 2007); (E) 各色圆叶牵牛; (F) 各色大丽花(Ohno et al., 2011); (G) 红肉苹果(Espley et al., 2009); (H) 彩叶草(Nguyen and Cin, 2009); (I) 紫色卷心菜(Yuan et al., 2009); (J) 紫色花椰菜(Chiu et al., 2010); (K) 红斑文心兰
Figure 4 Examples of commonly seen plant color mutants (some graphs were modified from relative references) (A) Red rice (Furukawa et al., 2007); (B) Variegated corn (Lazarow et al., 2013); (C) White grape; (D) Purple sweet potato (Mano et al., 2007); (E) Common morning glory; (F) Dahlia (Ohno et al., 2011); (G) Red fleshed apple (Espley et al., 2009); (H) Coleus (Nguyen and Cin, 2009); (I) Purple cabbage (Yuan et al., 2009); (J) Purple cauliflower (Chiu et al., 2010); (K) Red spotted dancing-doll orchid
| 植物 类别 | 物种名 | 颜色变异品种 | 突变位点 | 相关分子机制 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 粮食 作物 | 水稻 (Oryza sativa) | 红米 ( | bHLH类调控基因; 结构基因DFR | 红色稻米含原花青素, 推测为祖先型性状。白色稻米含有Rc或Rd位点的突变。其中Rc为bHLH类转录因子, 而Rd属于结构基因DFR。 | Sweeney et al., 2006; Furukawa et al., 2007 |
| 玉米 (Zea mays) | 红色及杂色品种 ( | MYB或bHLH类调控基因; 众多结构基因 | 玉米粒的颜色由表皮的鞣红和糊粉层的花青素共同构成。其祖先状态被认为是红紫色品种。玉米基因组中转座子在类黄酮相关的基因附近频繁活动, 使得这些基因常常失去或恢复活性, 而形成各种杂色表型。 | McClintock, 1950; Mol et al., 1998; Lazarow et al., 2013 | |
| 红薯 (Ipomoea batatas) | 紫薯 ( | MYB类调控基因 | 日常食用的红薯块根为白色到橙色, 不含色素或含类胡萝卜素。紫薯中则积累了不同程度的花青素。研究表明, 这是由于IbMYB1在紫薯块根中特异表达, 使块根中的花青素代谢途径被上调所致。 | Mano et al., 2007 | |
| 蔬菜 | 花椰菜 (Brassica oleracea var. botrytis) | 紫色花 椰菜 ( | MYB类调控基因 | 紫色品种中BoMYB2的启动子被插入1个转座子, 引起BoMYB2在球茎中大量表达, 球茎中的花青素代谢途径被上调。 | Chiu et al., 2010 |
| 卷心菜 (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) | 紫色卷 心菜 ( | MYB或bHLH类调控基因 | 紫色卷心菜中花青素代谢途径的正调控因子BoMYB2和 BoTT8表达显著提高, 而负调控因子BoMYB3的表达反而有所降低。 | Yuan et al., 2009 | |
| 水果 | 苹果 (Malus x domestica) | 红肉苹果 ( | MYB类调控基因 | 苹果一般为红皮白肉, 但自然界中也有红肉的品种。研究表明, 红肉苹果中MdMYB10的启动子近端区一处短片段发生了串联重复, 而此短片段中正好含有Md- MYB10蛋白的自身调控元件, 造成了MdMYB10基因可以正调控自身的表达, 形成无节制的自身正反馈。 | Espley et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2013a |
| 葡萄 (Vitis vinifera) | 紫皮和绿皮葡萄 ( | MYB类调控基因 | 葡萄总体上分为红黑皮和绿皮两个类群, 葡萄皮的颜色直接决定了葡萄酒的颜色。研究表明, 红黑皮为葡萄的祖先状态, 而白皮品种是由于其花青素特异调控基因Vv- MYBA1和VvMYBA2同时突变导致花青素特异结构基因3GT不能正常表达引起。 | Walker et al., 2007 | |
| 观赏 植物 | 文心兰 (Oncidium ‘Gower Ramsey’) | 花瓣上的花纹 ( | MYB类调控基因 | 文心兰的花为黄色背景带红色纹理。研究表明, 黄色背景部位缺乏花青素, 是由于OgMYB1在黄色部分不表达, 导致花青素代谢途径的2个结构基因OgCHI和Og- DFR不能表达。 | Chiou and Yeh, 2008 |
| 圆叶牵牛 (Ipomoea purpurea) | 多种花色着色形式 ( | MYB、bHLH或WDR类调控基因; 众多结构基因 | 圆叶牵牛具有极其多样的着色模式, 其变异涉及花青素代谢途径几乎所有的调控基因和结构基因, 大都由转座子的活动引起。它的野生型为蓝紫色, 红色为F3'H的突变引起, 白色和杂色品种则可以由众多其它基因上的突变引起。 | Hoshino et al., 2001, 2003; Clegg and Durbin, 2003; Morita et al., 2006; Park et al., 2007 | |
| 大丽花 (Dahlia variabilis) | 多种花色着色形式 ( | bHLH类调控基因 | 野生型大丽花为橙红色, 但其bHLH类调控基因被插入1个转座子后就可以形成黄底橙斑的杂色形式。这种杂色大丽花由于转座子的切离会发生后代花色分离。转座子非移码性切离可以产生完全回复的橙红色表型, 移码性切离会产生完全突变的黄色表型; 转座子不切离则后代将保留亲代黄底橙斑的杂色形式。 | Ohno et al., 2011 | |
| 彩叶草 (Solenostemon scutellarioides) | 叶片具丰富的着色形式 ( | 发育和环境信号联合导致花青素的不同程度表达引起 | 彩叶草由于叶色绚丽也被列为观赏植物。其多样的叶色其实是叶绿素和花青素不同比例组合的结果, 这种比例组合受到发育和环境信号的共同调控。 | Nguyen and Cin, 2009 |
表2 生活中常见颜色变异品种的已知分子机制
Table 2 Known molecular mechanisms responsible for common color mutants in cultivated plants
| 植物 类别 | 物种名 | 颜色变异品种 | 突变位点 | 相关分子机制 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 粮食 作物 | 水稻 (Oryza sativa) | 红米 ( | bHLH类调控基因; 结构基因DFR | 红色稻米含原花青素, 推测为祖先型性状。白色稻米含有Rc或Rd位点的突变。其中Rc为bHLH类转录因子, 而Rd属于结构基因DFR。 | Sweeney et al., 2006; Furukawa et al., 2007 |
| 玉米 (Zea mays) | 红色及杂色品种 ( | MYB或bHLH类调控基因; 众多结构基因 | 玉米粒的颜色由表皮的鞣红和糊粉层的花青素共同构成。其祖先状态被认为是红紫色品种。玉米基因组中转座子在类黄酮相关的基因附近频繁活动, 使得这些基因常常失去或恢复活性, 而形成各种杂色表型。 | McClintock, 1950; Mol et al., 1998; Lazarow et al., 2013 | |
| 红薯 (Ipomoea batatas) | 紫薯 ( | MYB类调控基因 | 日常食用的红薯块根为白色到橙色, 不含色素或含类胡萝卜素。紫薯中则积累了不同程度的花青素。研究表明, 这是由于IbMYB1在紫薯块根中特异表达, 使块根中的花青素代谢途径被上调所致。 | Mano et al., 2007 | |
| 蔬菜 | 花椰菜 (Brassica oleracea var. botrytis) | 紫色花 椰菜 ( | MYB类调控基因 | 紫色品种中BoMYB2的启动子被插入1个转座子, 引起BoMYB2在球茎中大量表达, 球茎中的花青素代谢途径被上调。 | Chiu et al., 2010 |
| 卷心菜 (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) | 紫色卷 心菜 ( | MYB或bHLH类调控基因 | 紫色卷心菜中花青素代谢途径的正调控因子BoMYB2和 BoTT8表达显著提高, 而负调控因子BoMYB3的表达反而有所降低。 | Yuan et al., 2009 | |
| 水果 | 苹果 (Malus x domestica) | 红肉苹果 ( | MYB类调控基因 | 苹果一般为红皮白肉, 但自然界中也有红肉的品种。研究表明, 红肉苹果中MdMYB10的启动子近端区一处短片段发生了串联重复, 而此短片段中正好含有Md- MYB10蛋白的自身调控元件, 造成了MdMYB10基因可以正调控自身的表达, 形成无节制的自身正反馈。 | Espley et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2013a |
| 葡萄 (Vitis vinifera) | 紫皮和绿皮葡萄 ( | MYB类调控基因 | 葡萄总体上分为红黑皮和绿皮两个类群, 葡萄皮的颜色直接决定了葡萄酒的颜色。研究表明, 红黑皮为葡萄的祖先状态, 而白皮品种是由于其花青素特异调控基因Vv- MYBA1和VvMYBA2同时突变导致花青素特异结构基因3GT不能正常表达引起。 | Walker et al., 2007 | |
| 观赏 植物 | 文心兰 (Oncidium ‘Gower Ramsey’) | 花瓣上的花纹 ( | MYB类调控基因 | 文心兰的花为黄色背景带红色纹理。研究表明, 黄色背景部位缺乏花青素, 是由于OgMYB1在黄色部分不表达, 导致花青素代谢途径的2个结构基因OgCHI和Og- DFR不能表达。 | Chiou and Yeh, 2008 |
| 圆叶牵牛 (Ipomoea purpurea) | 多种花色着色形式 ( | MYB、bHLH或WDR类调控基因; 众多结构基因 | 圆叶牵牛具有极其多样的着色模式, 其变异涉及花青素代谢途径几乎所有的调控基因和结构基因, 大都由转座子的活动引起。它的野生型为蓝紫色, 红色为F3'H的突变引起, 白色和杂色品种则可以由众多其它基因上的突变引起。 | Hoshino et al., 2001, 2003; Clegg and Durbin, 2003; Morita et al., 2006; Park et al., 2007 | |
| 大丽花 (Dahlia variabilis) | 多种花色着色形式 ( | bHLH类调控基因 | 野生型大丽花为橙红色, 但其bHLH类调控基因被插入1个转座子后就可以形成黄底橙斑的杂色形式。这种杂色大丽花由于转座子的切离会发生后代花色分离。转座子非移码性切离可以产生完全回复的橙红色表型, 移码性切离会产生完全突变的黄色表型; 转座子不切离则后代将保留亲代黄底橙斑的杂色形式。 | Ohno et al., 2011 | |
| 彩叶草 (Solenostemon scutellarioides) | 叶片具丰富的着色形式 ( | 发育和环境信号联合导致花青素的不同程度表达引起 | 彩叶草由于叶色绚丽也被列为观赏植物。其多样的叶色其实是叶绿素和花青素不同比例组合的结果, 这种比例组合受到发育和环境信号的共同调控。 | Nguyen and Cin, 2009 |
| 1 | 戴思兰, 黄河, 付建新, 洪艳 (2013). 观赏植物分子育种研究进展. 植物学报 48, 589-607. |
| 2 | 胡可, 韩科厅, 戴思兰 (2010). 环境因子调控植物花青素苷合成及呈色的机理. 植物学报 45, 307-317. |
| 3 | 黄金霞, 王亮生, 李晓梅, 鲁迎青 (2006). 花色变异的分子基础与进化模式研究进展. 植物学通报 23, 321-333. |
| 4 | 王璐, 戴思兰, 金雪花, 黄河, 洪艳 (2014). 植物花青素苷转运机制的研究进展. 生物工程学报 30, 848-863. |
| 5 | Albert NW, Davies KM, Lewis DH, Zhang H, Montefiori M, Brendolise C, Boase MR, Ngo H, Jameson PE, Sch- winn KE (2014). A conserved network of transcriptional activators and repressors regulates anthocyanin pigment- ation in eudicots.Plant Cell 26, 962-980. |
| 6 | Appelhagen I, Nordholt N, Seidel T, Spelt K, Koes R, Quattrochio F, Sagasser M, Weisshaar B (2015). TRANS- PARENT TESTA 13 is a tonoplast P3A-ATPase required for vacuolar deposition of proanthocyanidins in Arabi- dopsis thaliana seeds.Plant J 82, 840-849. |
| 7 | Chiou CY, Yeh KW (2008). Differential expression of MYB gene (OgMYB1) determines color patterning in floral tissue of Oncidium Gower Ramsey.Plant Mol Biol 66, 379-388. |
| 8 | Chiu LW, Zhou X, Burke S, Wu X, Prior RL, Li L (2010) The purple cauliflower arises from activation of a MYB transcription factor.Plant Physiol 154, 1470-1480. |
| 9 | Clegg MT, Durbin ML (2003). Tracing floral adaptations from ecology to molecules.Nat Rev Genet 4, 206-215. |
| 10 | Davies KM, Albert NW, Schwinn KE (2012). From landing lights to mimicry: the molecular regulation of flower colour- ation and mechanisms for pigmentation patterning.Funct Plant Biol 39, 619-638. |
| 11 | Dixon RA, Achnine L, Kota P, Liu CJ, Reddy MS, Wang L (2002). The phenylpropanoid pathway and plant defen- ce—a genomics perspective.Mol Plant Pathol 3, 371-390. |
| 12 | Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, Weisshaar B, Martin C, Lepiniec L (2010). MYB transcription factors in Arabi- dopsis.Trends Plant Sci 15, 573-581. |
| 13 | Espley RV, Brendolise C, Chagne D, Kutty-Amma S, Green S, Volz R, Putterill J, Schouten HJ, Gardiner SE, Hellens RP, Allan AC (2009). Multiple repeats of a promoter segment causes transcription factor autoregula- tion in red apples.Plant Cell 21, 168-183. |
| 14 | Furukawa T, Maekawa M, Oki T, Suda I, Iida S, Shimada H, Takamure I, Kadowaki KI (2007). The Rc and Rd genes are involved in proanthocyanidin synthesis in rice pericarp.Plant J 49, 91-102. |
| 15 | Gomez C, Conejero G, Torregrosa L, Cheynier V, Terrier N, Ageorges A (2011). In vivo grapevine anthocyanin transport involves vesicle-mediated trafficking and the contribution of anthoMATE transporters and GST.Plant J 67, 960-970. |
| 16 | Grotewold E, Drummond BJ, Bowen B, Peterson T (1994). The myb-homologous P gene controls phlobap- hene pigmentation in maize floral organs by directly activating a flavonoid biosynthetic gene subset.Cell 76, 543-553. |
| 17 | Hichri I, Barrieu F, Bogs J, Kappel C, Delrot S, Lau- vergeat V (2011). Recent advances in the transcriptional regulation of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway.J Exp Bot 62, 2465-2483. |
| 18 | Hoshino A, Johzuka-Hisatomi Y, Iida S (2001). Gene duplication and mobile genetic elements in the morning glories.Gene 265, 1-10. |
| 19 | Hoshino A, Morita Y, Choi JD, Saito N, Toki K, Tanaka Y, Iida S (2003). Spontaneous mutations of the flavonoid 3'-hydroxylase gene conferring reddish flowers in the three morning glory species.Plant Cell Physiol 44, 990-1001. |
| 20 | Jaakola L (2013). New insights into the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in fruits.Trends Plant Sci 18, 477-483. |
| 21 | Koes R, Verweij W, Quattrocchio F (2005). Flavonoids: a colorful model for the regulation and evolution of bio- chemical pathways.Trends Plant Sci 10, 236-242. |
| 22 | Lazarow K, Doll ML, Kunze R (2013). Molecular biology of maize Ac/Ds elements: an overview. In: Peterson T, ed. Plant Transposable Elements: Methods and Protocols. New York: Humana Press. pp. 59-82. |
| 23 | Lepiniec L, Debeaujon I, Routaboul JM, Baudry A, Pourcel L, Nesi N, Caboche M (2006). Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids.Annu Rev Plant Biol 57, 405-430. |
| 24 | Li Q, Zhao P, Li J, Zhang C, Wang L, Ren Z (2014). Genome-wide analysis of the WD-repeat protein family in cucumber and Arabidopsis.Mol Genet Genomics 289, 103-124. |
| 25 | Li YY, Mao K, Zhao C, Zhao XY, Zhang HL, Shu HR, Hao YJ (2012). MdCOP1 ubiquitin E3 ligases interact with MdMYB1 to regulate light-induced anthocyanin biosyn- thesis and red fruit coloration in apple.Plant Physiol 160, 1011-1022. |
| 26 | Lu YQ, Du J, Tang JY, Wang F, Zhang J, Huang JX, Liang WF, Wang LS (2009). Environmental regulation of floral anthocyanin synthesis in Ipomoea purpurea.Mol Ecol 18, 3857-3871. |
| 27 | Mano H, Ogasawara F, Sato K, Higo H, Minobe Y (2007). Isolation of a regulatory gene of anthocyanin biosynthesis in tuberous roots of purple-fleshed sweet potato.Plant Physiol 143, 1252-1268. |
| 28 | Matsui K, Umemura Y, Ohme-Takagi M (2008). AtMYBL2, a protein with a single MYB domain, acts as a negative regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis.Plant J 55, 954-967. |
| 29 | McClintock B (1950). The origin and behavior of mutable loci in maize.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 36, 344-355. |
| 30 | Miller R, Owens SJ, Rorslett B (2011). Plants and colour: flowers and pollination.Opt Laser Technol 43, 282-294. |
| 31 | Mol J, Grotewold E, Koes R (1998). How genes paint flowers and seeds.Trends Plant Sci 3, 212-217. |
| 32 | Morita Y, Saitoh M, Hoshino A, Nitasaka E, Iida S (2006). Isolation of cDNAs for R2R3-MYB, bHLH and WDR transcriptional regulators and identification of c and ca mutations conferring white flowers in the Japanese mor- ning glory.Plant Cell Physiol 47, 457-470. |
| 33 | Murre C, Bain G, Vandijk MA, Engel I, Furnari BA, Massari ME, Matthews JR, Quong MW, Rivera RR, Stuiver MH (1994). Structure and function of helix- loop-helix proteins.BBA-Gene Struct Expr 1218, 129-135. |
| 34 | Neer EJ, Schmidt CJ, Nambudripad R, Smith TF (1994). The ancient regulatory-protein family of WD-repeat pro- teins.Nature 371, 297-300. |
| 35 | Nguyen P, Cin VD (2009). The role of light on foliage colour development in coleus (Solenostemon scutellarioides (L.) Codd).Plant Physiol Bioch 47, 934-945. |
| 36 | Ohno S, Hosokawa M, Hoshino A, Kitamura Y, Morita Y, Park KI, Nakashima A, Deguchi A, Tatsuzawa F, Doi M, Iida S, Yazawa S (2011). A bHLH transcription factor, DvIVS, is involved in regulation of anthocyanin synthesis in dahlia (Dahlia variabilis).J Exp Bot 62, 5105-5116. |
| 37 | Park KI, Ishikawa N, Morita Y, Choi JD, Hoshino A, Iida S (2007). A bHLH regulatory gene in the common morning glory, Ipomoea purpurea, controls anthocyanin biosynthe- sis in flowers, proanthocyanidin and phytomelanin pig- mentation in seeds, and seed trichome formation.Plant J 49, 641-654. |
| 38 | Paz-Ares J, Ghosal D, Wienand U, Peterson PA, Saedler H (1987). The regulatory c1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homology to myb proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activators.EMBO J 6, 3553-3558. |
| 39 | Pires N, Dolan L (2010). Origin and diversification of basic helix-loop-helix proteins in plants.Mol Biol Evol 27, 862-874. |
| 40 | Poustka F, Irani NG, Feller A, Lu Y, Pourcel L, Frame K, Grotewold E (2007). A trafficking pathway for anthocya- nins overlaps with the endoplasmic reticulum-to-vacuole protein-sorting route in Arabidopsis and contributes to the formation of vacuolar inclusions.Plant Physiol 145, 1323-1335. |
| 41 | Prouse MB, Campbell MM (2012). The interaction between MYB proteins and their target DNA binding sites.BBA- Gene Regul Mech 1819, 67-77. |
| 42 | Quattrocchio F, Verweij W, Kroon A, Spelt C, Mol J, Koes R (2006). PH4 of petunia is an R2R3 MYB protein that activates vacuolar acidification through interactions with basic-helix-loop-helix transcription factors of the antho- cyanin pathway.Plant Cell 18, 1274-1291. |
| 43 | Ramsay NA, Glover BJ (2005). MYB-bHLH-WD40 protein complex and the evolution of cellular diversity.Trends Plant Sci 10, 63-70. |
| 44 | Saito N, Tatsuzawa F, Yoda K, Yokoi M, Kasahara K, Iida S, Shigihara A, Honda T (1995). Acylated cyanidin gly- cosides in the violet-blue flowers of Ipomoea purpurea.Phytochemistry 40, 1283-1289. |
| 45 | Sweeney MT, Thomson MJ, Pfeil BE, McCouch S (2006). Caught red-handed: Rc encodes a basic helix-loop-helix protein conditioning red pericarp in rice.Plant Cell 18, 283-294. |
| 46 | Tanaka Y, Sasaki N, Ohmiya A (2008). Biosynthesis of plant pigments: anthocyanins, betalains and carotenoids.Plant J 54, 733-749. |
| 47 | Tapas AR, Sakarkar DM, Kakde RB (2008). Flavonoids as nutraceuticals: a review.Trop J Pharm Res 7, 1089-1099. |
| 48 | van Nocker S, Ludwig P (2003). The WD-repeat protein superfamily in Arabidopsis: conservation and divergence in structure and function.BMC Genomics 4, 50. |
| 49 | Walker AR, Davison PA, Bolognesi-Winfield AC, James CM, Srinivasan N, Blundell TL, Esch JJ, Marks MD, Gray JC (1999). The TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA1 locus, which regulates trichome differentiation and antho- cyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis, encodes a WD40 repeat protein.Plant Cell 11, 1337-1349. |
| 50 | Walker AR, Lee E, Bogs J, McDavid DAJ, Thomas MR, Robinson SP (2007). White grapes arose through the mutation of two similar and adjacent regulatory genes.Plant J 49, 772-785. |
| 51 | Wang HL, Guan S, Zhu ZX, Wang Y, Lu YQ (2013a). A valid strategy for precise identifications of transcription factor binding sites in combinatorial regulation using bio- informatic and experimental approaches.Plant Methods 9, 34. |
| 52 | Wang ZG, Meng D, Wang AD, Li TL, Jiang SL, Cong PH, Li TZ (2013b). The methylation of the PcMYB10 promoter is associated with green-skinned sport in max red bartlett pear.Plant Physiol 162, 885-896. |
| 53 | Winkel-Shirley B (2001). Flavonoid biosynthesis. A colorful model for genetics, biochemistry, cell biology, and bio- technology.Plant Physiol 126, 485-493. |
| 54 | Xu W, Grain D, Bobet S, Le Gourrierec J, Thevenin J, Kelemen Z, Lepiniec L, Dubos C (2014). Complexity and robustness of the flavonoid transcriptional regulatory network revealed by comprehensive analyses of MYB- bHLH-WDR complexes and their targets in Arabidopsis seed.New Phytol 202, 132-144. |
| 55 | Yoshida K, Kondo T, Okazaki Y, Katou K (1995). Cause of blue petal colour.Nature 373, 291. |
| 56 | Yuan YX, Chiu LW, Li L (2009). Transcriptional regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in red cabbage.Planta 230, 1141-1153. |
| 57 | Zhang F, Gonzalez A, Zhao M, Payne CT, Lloyd A (2003). A network of redundant bHLH proteins functions in all TTG1-dependent pathways of Arabidopsis.Development 130, 4859-4869. |
| 58 | Zhao J, Dixon RA (2010). The 'ins' and 'outs' of flavonoid transport.Trends Plant Sci 15, 72-80. |
| 59 | Zhu ZX, Wang HL, Wang YT, Guan S, Wang F, Tang JY, Zhang RJ, Xie LL, Lu YQ (2015). Characterization of the cis elements in the proximal promoter regions of the an- thocyanin pathway genes reveals a common regulatory logic that governs pathway regulation.J Exp Bot 66, 3775-3789. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
